Types of Dental Implant Systems
Simple Solutions
Our success rate is one of the best in the dental industry, reaching a remarkable high of 99.4%¹.; dentists praise the OsteoCare system for being one of the “simple” and “easy to use” types of dental implant systems and ideal for every clinical scenario. The success rate stems from precision engineering with ease of use at the forefront of each design.

Maxi Z Family
OsteoCare like to refer to the Maxi Z range of dental implants as the all-rounder choice of types of implants in dentistry. The range has an implant for a wide range of clinical scenarios.
With One & Two Piece options it is flexible and cost effective for the dentist and patient.
The tapered designs allows for transmucossal placement, if desired, which is less traumatic for the patient and preserves the bone and soft tissue².
Read more
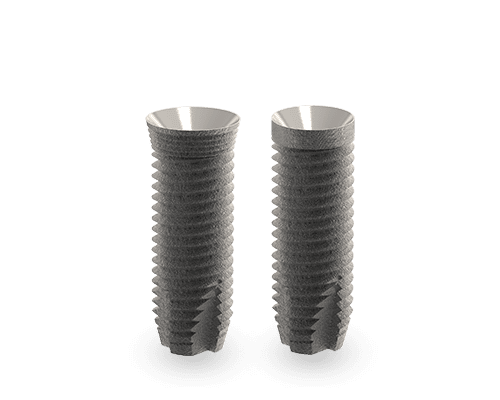
One-Piece
The One Piece is every patient’s dream as it removes the need for second stage surgery. The One -Piece implant is made from a solid piece of Titanium with integrated abutment, there is no need for extra prosthetics. All that is required is preparation of the abutment section and the crown, making it incredible cost effective. The Platform design of the Maxi Z One-piece gives better aesthetic emergence profile, especially in the anterior aesthetic zone.
Two-Piece
The Maxi Z Two-Piece Dental Implant is a dynamic implant with multiple restorative options. The tapered design lends itself particularly well to immediate placement in a post extraction socket as well as atrophic ridges.
Immediate loading is also possible as the tapered design allows for good initial stability even in poor quality bone3-4. The Maxi Z Two-piece can placement with or without raising a flap, dependant on the clinicians preference.
Flat-End
The Maxi Z Flat-End Dental Implant has all the features of the Maxi Z Two-Piece with the added benefit of a flat tip, which allows for sinus floor augmentation without perforating the Schneiderian membrane in cases of vertical bone. The Maxi Z Flat-End can be used in conjunction with the OsteoCare flat-end osteotomes if there is a need to break the sinus floor. The Maxi Z Flat-end starts in lengths of 6.5mm.

Mini/Midi Duo
OsteoCare Mini & Midi Ball & post type dental implants are ideal in narrow atrophic ridges as they start in diameters of 2.35mm.
The implants may be placed in a single-stage transgingival procedure, if desired.
In certain cases the Implant can be placed using just pilot drill, making this a less invasive treatment option of implant systems in dentistry.
Read more
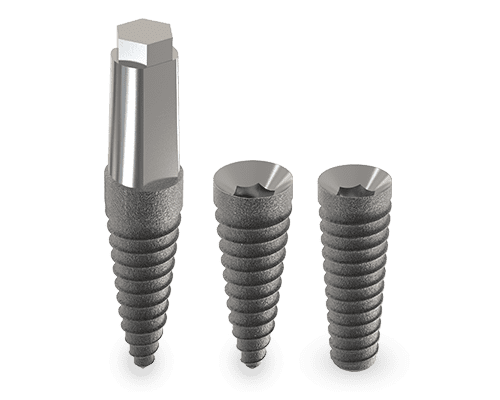
Mini/Midi Post
OsteoCare Mini/Midi Post-Type Dental Implant are made from one piece of titanium with an integrated abutment. They are an extremely cost effect solution for certain cases, as there is no need to purchase other OsteoCare components. They are commonly used in cases where immediate loading is indicate. The tapered design along with the small diameters makes them a perfect implant for use in narrow atrophic ridges.
- Quick and simple implant placement due to conical shape
- Maximum primary stability in all types of bone due to the buttress threads design
- Atraumatic implant placement, even in cortical bone
- Bone expansion and compression by rotation making it less traumatic for the patient
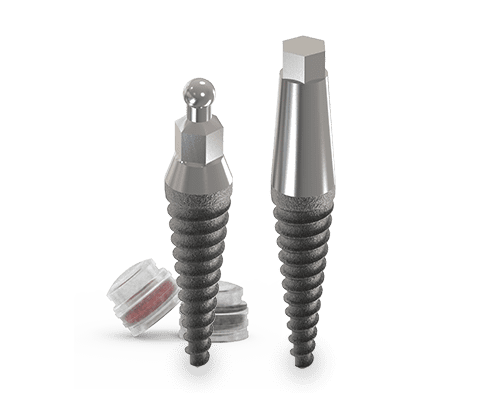
Mini/Midi Ball
OsteoCare Mini and Midi One-Piece Ball-Type implants have demonstrated excellent long-term survival, marginal bone response, and soft tissue conditions with immediately loaded mandibular overdentures.
The primary stability of conical implants is greater than cylindrical implants. They have proved to be a viable and predictable treatment option for completely edentulous mandibles in stabilising overdentures.
The conical shaped mini-implants have advantages such as mechanical retention and good primary stability5. The conical implant design in conjunction with an undersized drill form leads to initial higher stability than conventional implants this was evident by the Periotest M values obtained.6-8
- Quick and simple implant placement due to conical shape
- Maximum primary stability in all types of bone due to the buttress threads design
- Atraumatic implant placement, even in cortical bone
- Bone expansion and compression by rotation making it less traumatic for the patient

GBA surface

No Touch Technique

One Drill Placement

O-Ring

The Classics
OsteoCare Classic Advanced and Advanced are conventional parallel two-piece implants, which are considered the most scientifically documented types of dental implants systems within the industry.
Brånemark was the first type of dental implants systems to use this shape implant dating back to 1965 and from there others have adopted the design in their implant systems in dentistry.
Read more
The Classic Advanced and Advanced implants are the original design form OsteoCare and are still as popular today as they were when the company was founded.
- Twin start thread allows for swift placement.
- Self tapping V shaped thread with reliefs that reduce mechanical load on the implants and advantageous to surrounding bone.
- Stability in all type of bone including type II and type III.
- Parallel Walled.
- Flared Head and Micro Grooves (Advanced implant only) allows for optimal emergence profile and improving bone resorption.

GBA surface

No Touch Technique

Twin Start Threads

System Features
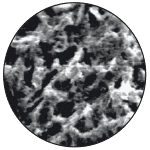
Grit Blasted & Acid Etched (GBA) Surface
Grit-blasting produces a defined macro-roughness surface and etching with mineral acid, which increases the micro-roughness surface. GBA enhances osseointegration and provides a 240% greater surface area than a traditional machined surface. All OsteoCare dental implants have a GBA surface.

“No Touch” Technique
OsteoCare’s carrier system enables storage without contact between the implant and vial known as the “No Touch” technique. No contact when transporting the implant to the osteotomy ensures the avoidance of possible contaminates.

One Drill Placement
Mini & Midi Dental Implants may be placed in a single-stage transgingival procedure. Dental implant placement surgery usually involves only minor preparation of the bone (osteotomy) using a profile drill and seating of the implant within the osteotomy. This is a less invasive treatment option.

Twin Start Thread
The advantages of the twin start thread are that the implants may be placed in poor quality bone, which radically enhances primary stability, and for type II or type III bone the opportunity for immediate or early load is maximised. Twin start thread allows for swift placement.
+ References
1. Based on Implant Sales year 2017-Present
2 Talwar, B. (2012). A Focus on Soft Tissue in Dental Implantology. The Journal of Indian Prosthodontic Society, [online] 12(3), pp.137-142. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3416938/ [Accessed 15 Jul. 2018].
3. Alves, C. and Neves, M. (2009). Tapered implants: from indications to advantages. PubMed, [online] pp.161-167. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19408478 [Accessed 7 Jun. 2018].
4. Wilson, T., Miller, R., Trushkowsky, R. and Dard, M. (2016). Tapered Implants in Dentistry. Advances in Dental Research, [online] 28(1), pp.4-9. Available at: http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/0022034516628868 [Accessed 17 Aug. 2018].
5. Attard NJ, Zarb GA. Long-term treatment outcomes in edentulous patients with implant overdentures: the Toronto study. Int J Prosthodont. 2004; 17: 425-433. 15. Dudic A, Mericske-Stern R. Retention mechanisms and prosthetic complications of implant-supported mandibular overdentures: long-term results. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2002; 4: 212-219.
6. 40. Gatti C, Haefliger W, Chiapasico M. Implant-retained mandibular overdentures with immediate loading: a prospective study of the ITI implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2000; 15: 383–388. 41. Chiapasco M, Abati S, Romeo E, Vogel G. Implant-retained mandibular overdentures with Branemark System MK II implants. A prospective comparative study between delayed and immediate loading. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001; 16: 537–546.
7. Morneburg TR, Proschel PA. Success rates of microimplants in edentulous patients with residual ridge resorption. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2008; 23: 270–276. 43. Romeo E, Lops D, Amorfini L, Chiapasco M, Ghisolfi M, Vogel G. Clinical and radiographic evaluation of small-diameter (3.3-mm) implants followed for 1–7 years: a longitudinal study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006; 17: 139–148.
8. Zarb GA, Schmitt A. Osseointegration for elderly patients: The Toronto study. Part II: The prosthetic results. J Prosthet Dent. 1994; 72: 559-568 9. Zarb GA, Schmitt A. The edentulous predicament II: The longitudinal effectiveness of implant-supported overdentures. J Am Dent Assoc. 1996; 127: 66-72. 10.Zahran A. Clinical evaluation of the OsteoCare Mini and Midi implants for immediate loading of mandibular overdentures. J Implant Dentistry Today. 2008; 2: 54–59.- Perfect for overdentures.